Fiber Fence Security System vs. Compact Radar: A Comprehensive Technical Comparison and Selection Guide
I. Overview
In the field of perimeter security, no single solution fits all scenarios. Different types of sensors and security measures have their own emphases, and selection must be based on the actual environment and security requirements. Global security experts generally agree that protecting high-value private assets and critical infrastructure requires a strategy of multi-sensor fusion and multi-level system integration to build a truly reliable perimeter protection system.
Developing an efficient multi-level security plan requires a deep understanding of potential threats and applicable technologies. This article will comprehensively compare fiber fence security systems and new compact security radars from multiple dimensions, including technical principles, deployment costs, system integration, and practical effectiveness, to help users make optimal decisions based on actual needs and budgets.
II. Analysis of Fiber Fence Security Systems
Fiber-based fence security systems are highly sensitive perimeter intrusion detection solutions that use optical fiber sensors embedded in fence structures to detect vibrations and deformations, enabling real-time alerts for intrusions such as climbing, cutting, or impact. This system is particularly suitable for high-security locations such as prisons, airports, and power plants.
Working Principle:
- Optical fibers are deployed in segments to achieve precise intrusion location detection.
- Sensors capture vibration signals in real time and generate alerts.
- Alarm information is uploaded to a network manager and integrated into VMS, SMS, or PSIM platforms.

III. Introduction to Compact Security Radar Technology
New compact security radars use advanced radio wave detection technology to detect and track moving targets in monitored areas in real time, providing early warnings to security personnel and giving them more time to respond.
Core Advantages:
- All-Weather Operation: Unaffected by adverse weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow.
- Wide-Area Monitoring: Large coverage per device with low deployment costs.
- Seamless Integration: Supports automatic linkage with PTZ cameras.
- AI Target Recognition: Utilizes the LGSS_AI algorithm box to distinguish between humans, vehicles, animals, and other targets.
- Flexible Deployment: Supports customizable alert zones and rules on GIS maps.

IV. Key Technical Comparison Between Fiber Systems and Radar Systems
Although both are intrusion detection devices, they differ fundamentally in warning mechanisms, deployment methods, and system capabilities:
1. Warning Capability
- Fiber System: Post-event alerts, triggered only after an intrusion occurs.
- Radar System: Pre-event warnings, capable of detecting approaching targets minutes in advance.
2. Installation and Scalability
- Fiber System: Complex installation, high cost, difficult to scale.
- Radar System: Quick deployment, high adaptability, easy scalability.
3. Target Positioning and Tracking
- Fiber System: Only supports zone alerts, unable to provide real-time positioning.
- Radar System: Provides GPS coordinate output and supports automatic camera tracking.
4. Intelligent Filtering and False Alarm Control
- Fiber System: Lacks AI recognition, prone to environmental interference.
- Radar System: Supports intelligent behavior analysis based on speed, motion trajectory, and duration.
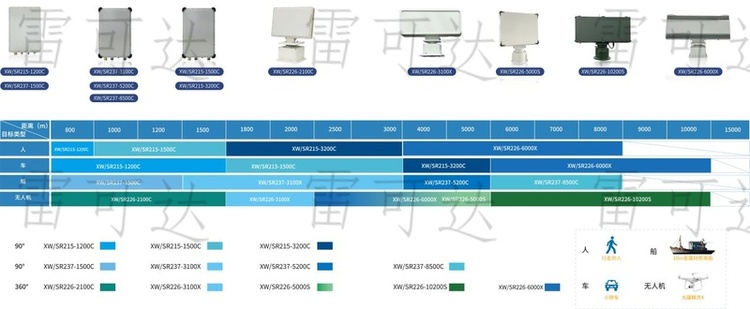
V. Practical Application Comparison: Perimeter Protection for Nuclear Power Plants
Assuming a perimeter length of 2,000 meters:
Fiber Fence Solution
- Equipment Cost: Approximately ¥250,000
- Functional Limitations: Only supports fence intrusion detection.
- Note: Does not include labor and physical fence construction costs.
Lakeda Radar Solution
- Option 1 (Basic Coverage): <¥100,000, includes radar, mount, and cables.
- Option 2 (Enhanced Version): <¥150,000, adds land and water target tracking capabilities.
VI. Conclusion and Recommendations
Both fiber fence systems and compact security radars are effective perimeter protection methods, but their applicable scenarios and return on investment differ significantly:
Core Advantages of Compact Security Radars:
- Higher cost-effectiveness, more economical deployment and maintenance.
- Capable of pre-event warnings and real-time target tracking.
- Supports AI behavior analysis and false alarm filtering.
- Seamlessly integrates with video systems for precise visual tracking.
- Flexible deployment strategies, supporting electronic maps and multi-scenario configurations.
In most modern security applications, compact surveillance radars demonstrate superior overall performance and scalability, making them an ideal choice for building intelligent perimeter protection systems.
Friendly Reminder: Security technology evolves rapidly. It is recommended to consult professional security advisors before finalizing your selection to obtain customized solutions and the latest technical information.
Further Reading
- Trends in Perimeter Security Technology and Multi-Sensor Fusion Solutions—China Security and Protection Industry Association
- Research on Smart Security and Multi-Sensor Fusion Technology—Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China
- Overview of Perimeter Intrusion Protection Technology Development—Google Scholar